AQUAPONIC UNIT DESIGN
• The main factors when deciding where to place a unit are: stability of ground; access to sunlight and shading; exposure to wind and rain; availability of utilities; and availability of a greenhouse or shading structure.
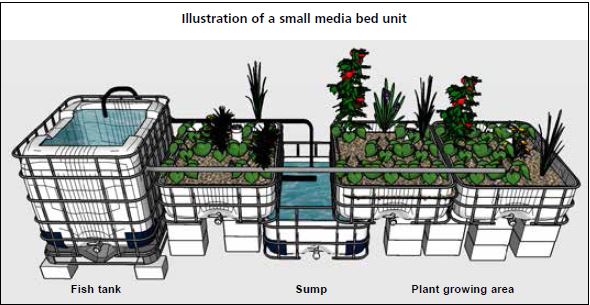
• There are three main types of aquaponics: the media bed method, also known as particulate bed; the nutrient film technique (NFT) method; and the deep water culture (DWC) method, also known as the raft method or floating system. The essential components for all aquaponic units are: the fish tank, the mechanical and biological filtration, the plant growing units (media beds, NFT pipes or DWC canals), and the water/air pumps.
• The media beds must: (i) be made of strong inert material; (ii) have a depth of about 30 cm; (iii) be filled with media containing a high surface area; (iv) provide adequate mechanical and biological filtration; (v) provide separate zones for different organisms to grow; and (vi) be sufficiently wetted through flood-and- drain or other irrigation techniques to ensure good filtration.
For NFT and DWC units, mechanical and biofiltration components are necessary in order to respectively remove the suspended solids and oxidize the dissolved wastes (ammonia to nitrate).
• For NFT units, the flow rate for each grow pipe should be 1-2 litres/minute to ensure good plant growth.
• For DWC units each canal should have a retention time of 1-4 hours.
• High DO concentration is essential to secure good fish, plant and bacteria growth. In the fish tank DO is supplied by means of air stones. Media bed units have an interface between the wet zone and dry zone that provides a high availability of atmospheric oxygen. In NFT units, additional aeration is provided into the biofilter, while in DWC air stones are positioned in the biofilter and plant canals.